IT Service Management AND Automation: Now That’s A Double Whammy Of Business-Enabling Goodness
A recent Forrester report helps IT infrastructure and operations (I&O) leaders understand the business and IT impact of service management and automation (SMA). While both IT service management (ITSM) and automation can be used effectively in isolation, I&O organizations should be seeking to use them in tandem for an "amplified" business impact.
The General Benefits Of Service Management And Automation
The general benefits of SMA can be divided between the I&O organization and the business, though these benefits often overlap:
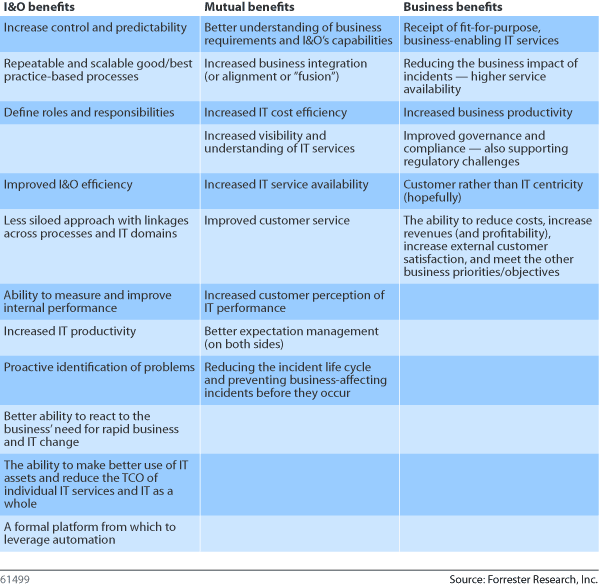
While SMA is much more than the adoption of IT infrastructure library (ITIL), the ITSM best practice framework, thinking and processes — ITIL's benefits are quite reflective of the general benefits of broader SMA. In a survey of 491 members of the USA chapter of the IT Service Management Forum (itSMF), Forrester found that organizations which adopted ITIL experience the following benefits:
- Improved staff productivity that allows the business to become more competitive (85%).
- Heightened quality of service that improves business uptime and customer experience (83%).
- Reduced operational costs to reinvest in new and innovative initiatives (41%).
- Improved reputation with the business (65%).
The Benefits Of Automation
Cloud computing and DevOps are accelerating the evolution of automated service management, with service management itself evolving to adapt to automation. There is a symbiotic relationship between these movements. Neither cloud computing nor DevOps is truly feasible without extreme automation, and automation needs the economic force of movements like cloud and DevOps to compel the market investment necessary to deliver capable technology solutions. It's becoming increasingly obvious that service management in any form will be impossible without significant improvements in automation and the inherent benefits:
- The acceleration of process execution.
- The reduction in human errors and the unwanted consequences.
- The ability to rapidly adapt as both business and IT needs change.
- Reduction in the cost of IT operations.
- The ability to proactively respond to the shrinking "available resource pool."
- Freeing highly skilled and knowledgeable staff from the repeatable, mundane tasks.
An automation example from the report is shown below:
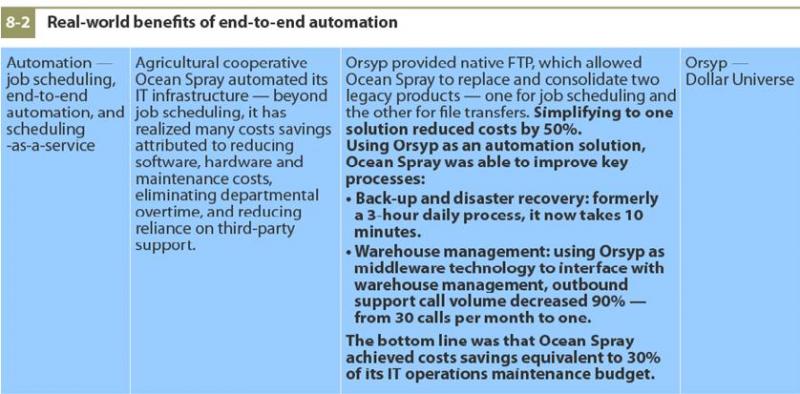
But remember that for a bad process with a bad business outcome, automation just lets you get to the bad outcome more quickly.
Combining Service Management And Automation Amplifies Benefits
While the SMA report looks in detail at service management and automation used in isolation, the benefits can be extended by using both disciplines in tandem. Self-help password resets is a common but powerful example; FastPass Corporation estimates the fully burdened cost of a password reset is $18 per support call, not factoring in loss of productivity. Other common examples include service catalog workflow, automation for provisioning, or remote support and chat (a chat example is shown below).
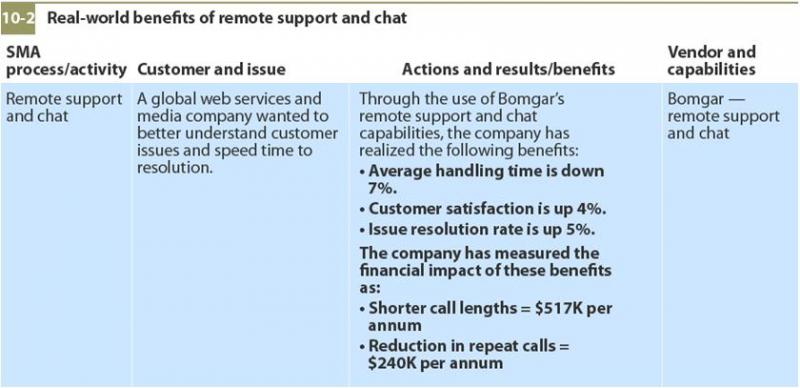
Leveraging automation for ITSM brings with it a number of benefit-enhancing advantages: It helps to remove people dependency, people costs, and human error; it speeds the time to enact a given process; and it results in a better IT service delivery experience and hopefully a better customer experience (and greater customer satisfaction).
In Forrester's opinion, automation is the future of IT service delivery (please don't read this as contradictory to my continued push for greater customer-centricity — the two aren't mutually exclusive) and as my esteemed colleague Glenn O’Donnell says:
What do you think?